In the early morning of December 15, Beijing time, the Federal Reserve announced to raise interest rates by 50 basis points, the federal funds rate range was raised to 4.25% - 4.50%, the highest since June 2006. In addition, the Fed forecasts the federal funds rate will peak at 5.1 percent next year, with rates expected to fall to 4.1 percent by the end of 2024 and 3.1 percent by the end of 2025.
The Fed has raised interest rates seven times since 2022, a total of 425 basis points, and the Fed funds rate is now at a 15-year high. The previous six rate hikes were 25 basis points on March 17, 2022; On May 5, it raised rates by 50 basis points; On June 16, it raised rates by 75 basis points; On July 28, it raised rates by 75 basis points; On September 22, Beijing time, the interest rate increased by 75 basis points. On November 3rd it raised rates by 75 basis points.
Since the outbreak of the novel coronavirus in 2020, many countries, including the US, have resorted to "loose water" to cope with the impact of the pandemic. As a result, the economy has improved, but inflation has soared. The world's major central banks have raised interest rates about 275 times this year, according to Bank of America, and more than 50 have made a single aggressive 75 basis point move this year, with some following the Fed's lead with multiple aggressive hikes.
With RMB depreciates nearly 15%, chemical imports will be even more difficult
The Federal Reserve took advantage of the dollar as the world's currency and raised interest rates sharply. Since the beginning of 2022, the dollar index has continued to strengthen, with a cumulative gain of 19.4% during the period. With the US Federal Reserve taking the lead in aggressively raising interest rates, a large number of developing countries are facing enormous pressures such as the depreciation of their currencies against the US dollar, capital outflow, rising financing and debt service costs, imported inflation, and volatility of commodity markets, and the market is increasingly pessimistic about their economic prospects.
The US dollar interest rate hikes have made the US dollar return, the US dollar appreciates, the currency depreciation of other countries, and the RMB will not be exceptions. Since the beginning of this year, the RMB has undergone a sharp depreciation, and the RMB depreciated by nearly 15%when the RMB exchange rate against the US dollar has minimized.
According to previous experience, after the depreciation of RMB, the petroleum and petrochemical industries, non-ferrous metals, real estate and other industries will experience a temporary slump. According to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, 32% of the country's varieties are still blank and 52% still rely on imports. Such as high-end electronic chemicals, high-end functional materials, high-end polyolefin, etc., it is difficult to meet the needs of economy and people's livelihood.
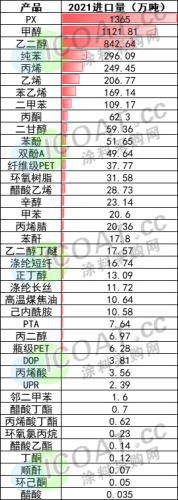
In 2021, the import volume of chemicals in my country exceeded 40 million tons, of which the import dependence of potassium chloride was as high as 57.5%, MMA's external dependence of exceeding 60%, and chemical raw materials such as PX and methanol imports exceeded 10 million tons in 2021.
In the field of coating, many raw materials are selected from overseas products. For example, Disman in the epoxy resin industry, Mitsubishi and Sanyi in the solvent industry; BASF, Japanese Flower Poster in the foam industry; Sika and Visber in the curing agent industry; DuPont and 3M in the wetting agent industry; Wak, Ronia, Dexian; Komu, Hunsmai, Connoos in the titanium pink industry; Bayer and Langson in the pigment industry.
The depreciation of the RMB will inevitably lead to an increase in the cost of imported chemical materials and compress the profitability of enterprises in multiple industries. At the same time as the cost of imports increases, the uncertainties of the epidemic are increasing, and it is even more difficult to get the high -end raw materials of imported imports.
Export -type enterprises have not been substantially favorable, and relatively competitive are not strong
Many people believe that the depreciation of currency is conducive to stimulating exports, which is good news for export companies. Commodities priced at US dollars, such as oil and soybeans, will "passively" increase prices, thereby increasing global production costs. Because the US dollar is valuable, the corresponding material exports will appear cheaper and export volume will increase. But in fact, this wave of global interest rate hikes also brought a depreciation of a variety of currencies.
According to incomplete statistics, 36 categories of currency in the world have depreciated at least one -tenth, and Turkish lira depreciates 95%. Vietnamese Shield, Thai baht, the Philippine Peso, and Korean Monsters have reached a new low in many years. The appreciation of RMB on non -US dollar currency, the depreciation of the renminbi is only relative to the US dollar. From the perspective of yen, euro, and British pounds, the yuan is still "appreciation". For export -oriented countries such as South Korea and Japan, the depreciation of the currency means the benefits of exports, and the depreciation of the renminbi is obviously not as competitive as these currencies, and the benefits obtained are not substantial.
Economists have pointed out that the current global concern currency tightening problem is mainly represented by the Fed's radical interest rate hike policy. The Fed's continued tightening monetary policy will have a spillover impact on the world, impacting the global economy. As a result, some emerging economies have destructive effects such as capital outflows, rising import costs, and depreciation of their currency in their country, and have pushed the possibility of large -scale debt defaults with high debt emerging economies. At the end of 2022, this interest rate hike may cause domestic import and export trade to be oppressed in two -way, and the chemical industry will have a deep impact. As for whether it can be relieved in 2023, it will depend on the common actions of multiple economies in the world, not individual performance.
Post time: Dec-20-2022